Express planner calculation explanation with examples
Concept definition
The express planner (EP) in PMI is a forecasting tool designed to automate the generation of monthly forecasts for ancillary revenue and labor hours. It helps users quickly generate projections based on historical data, growth assumptions, and productivity metrics.
Formula or logic
Step 0: Settings are configured (See step-by-step guide)
Step 1: Determine room revenue baseline
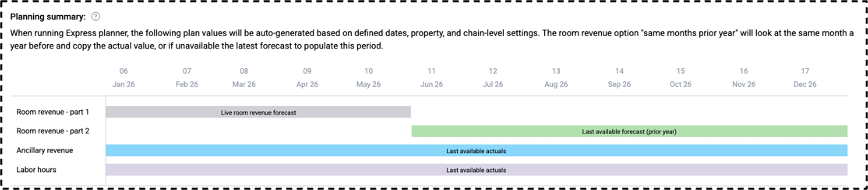
EP begins by establishing the room revenue baseline for the forecast period. Default source for room revenue – part 1 (first months of forecast) is: Live room revenue forecast
If room revenue – part 2 is enabled, the months at the end of the forecast will source based on the setting chosen. (last available forecast, or actuals from a previous year)
Step 2: Calculate Ancillary Revenue Using Historical Proportions
EP calculates ancillary revenue by applying historical ratios to the room revenue baseline. The historical ratio between room revenue and ancillary revenue is calculated for the baseline chosen for ancillary revenue under rule 3 in the general setting management:
Options include:
- Last submitted forecast
- Last available actuals
- Actuals (prior year)
This proportion will then be applied to the live forecast room revenue for the period that the express planner is being run, to calculate the forecasted non-room revenue and total revenue. The option selected in rule 3 under ancillary revenue settings will determine whether a monthly specific proportion or the yearly average will apply.
Step 3: Apply growth adjustment to ancillary revenue
EP allows users to apply a growth percentage to the calculated ancillary revenue to reflect expected performance changes.
If a percentage was specified with which ancillary revenue will grow, this growth will be added to the total after it has been forecasted as per step 2.
Step 4: Split total revenue into divisions
Ep will then split revenue based on the divisions set up in PMI.
Before the forecasted non-room revenue can be separated into divisions, the split ratio that was used in the historical year that was selected in rule 3 under general settings will be determined.
These proportions will then be applied to the forecasted total revenue (calculated in step 3) to calculate the forecasted divisional revenue.
Step 5: Split divisional revenue into departments
The divisional revenue is then split into departments.
Rule 4 in ancillary revenue will determine the baseline data used to determine the proportional split of the divisional revenue into departments. This percentage split will then be applied to the forecasted divisional revenue calculated in step 4 to determine the forecasted departmental revenue.
If the proportional split calculated above is not a reliable method to determine the revenue for a specific department, you can revise this in rule 5 under ancillary revenue settings. Choose between guest nights, room nights, total revenue and room revenue as a revenue driver. You can then assign a value to this driver. Room nights and guest nights will be a monetary value, while room revenue and total revenue will be a percentage.
The revenue calculated for the department specified in rule 5 will be deducted from the divisional revenue. The remaining revenue will then be split into departments.
Step 6: Segment departmental revenue (if applicable)
For departments where the “Segments” option under Settings in the budget & forecast page has been selected, the departmental revenue calculated in rule 4 will be split into these segments.
The split per department for the past 12 months is then determined.
The proportional split calculated will then be applied to the departmental revenue calculated to determine the revenue per segment.
Step 7: Calculate productivity
The option selected in rule 2 under Labor hour settings will determine the data used to calculate the productivity for each labor department. The productivity figure will then be used to calculate the forecasted hours based on the cost driver selected in the cockpit for each department.
- If you’ve selected the option “Use same month productivity from last available actuals ”, the data from the most recent 12 months will be used. If you’ve selected to apply period locking to actuals and the last month has not yet been locked, it will not be considered when determining the past 12 months. If the previous month has been locked, it will be included in the 12 months.
- If you’ve selected the option “Use annual average for all months from the baseline”, the productivity will be calculated based on the historical data that you selected in rule 1.
- If you’ve selected the option “Use productivity from same month in baseline”, the productivity will be calculated for each month based on the historical data that you’ve selected in rule 3 under General set-up settings.
In rule 3 under Labor hour settings, you can set a percentage by which the productivity for each department must be adjusted. This percentage can be positive or negative. A positive adjustment will give less hours, and therefore lower labor costs. A negative adjustment will result in more hours being forecasted, leading to higher labor costs.
Step 8: Calculate forecasted labor hours
The adjusted productivity can now be applied to the forecasted cost driver for the relevant departments to calculate the hours.
Step 9: Allocate outsourced labor hours
EP splits forecasted labor hours into in-house and outsourced based on historical proportions in the baseline selected for Labor hours.
Step 10: Update ancillary live forecast for all profit centers.
.EP updates the live forecast for ancillary revenue departments with the newly forecasted revenue figures.
Step 11: Copy manually entered forecast expenses
When EP is forecasting for a period which does not exist in the last submitted forecast, it will copy manually entered expenses from the previously submitted forecast to the new forecasting period. Eg: when forecasting for Feb 2026 (where previously submitted forecast was up to Jan 2026) then EP will copy all manually entered forecast expenses from Jan 2025 to Jan 2026 work-in-progress forecast. If a last submitted forecast does not exist for Jan 2025, it will check if one exists for Jan 2024. EP will only copy values for accounts which do not have formulas linked to them in P&L module.
Worked examples
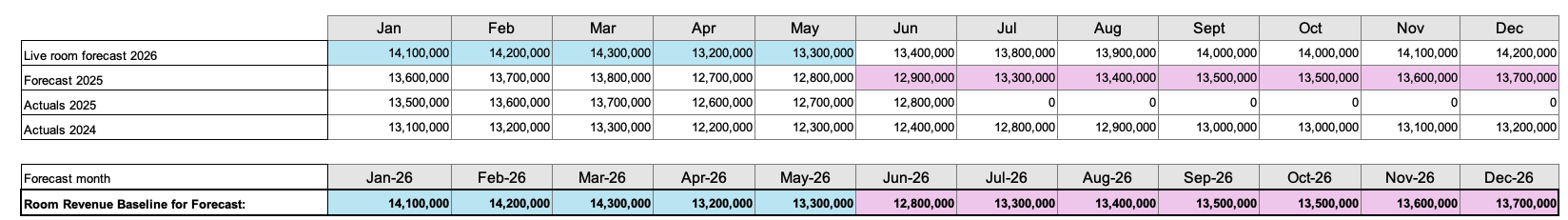
Example, Step 1: Determine room revenue baseline
Eg: for a six month forecast from Jan 2026-Dec 2026 (created in July 2025) where:
Room revenue – part 1 was set to 5 month (using live room forecast)
Room revenue – part 2 for baseline, the sourcing of the baseline revenue would look like this:
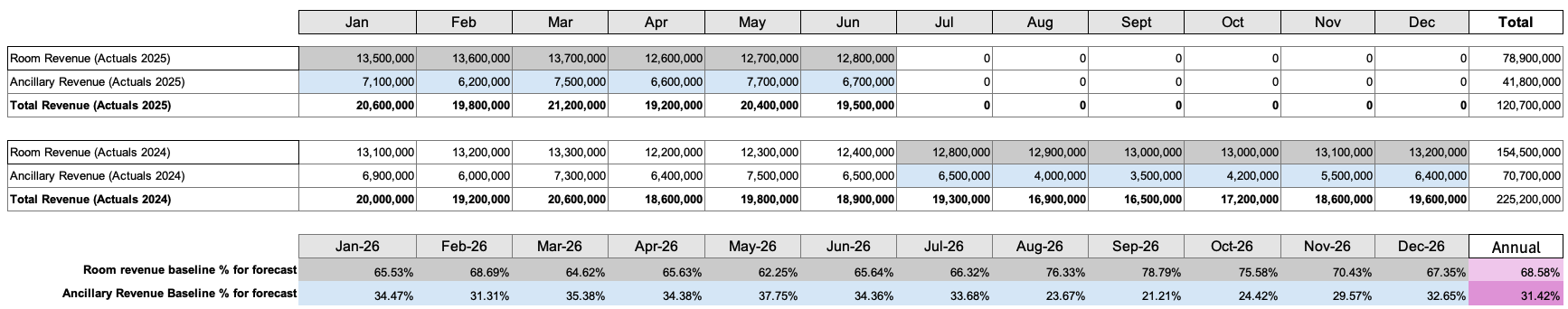
Step 2: Calculate ancillary revenue using historical proportions
Eg: for a twelve-month forecast from Jan 2026-Dec 2026 (created in July 2025) where last available actuals is chosen for baseline, the calculation of the historical ratio is performed as shown below. EP uses Global account category to differentiate between room revenue and ancillary revenue for this step.
Formula: Room Revenue baseline % equals Room revenue from baseline period divided by Total Revenue from baseline period. Ancillary Revenue baseline % equals Ancillary revenue from baseline period divided by Total Revenue from baseline period.
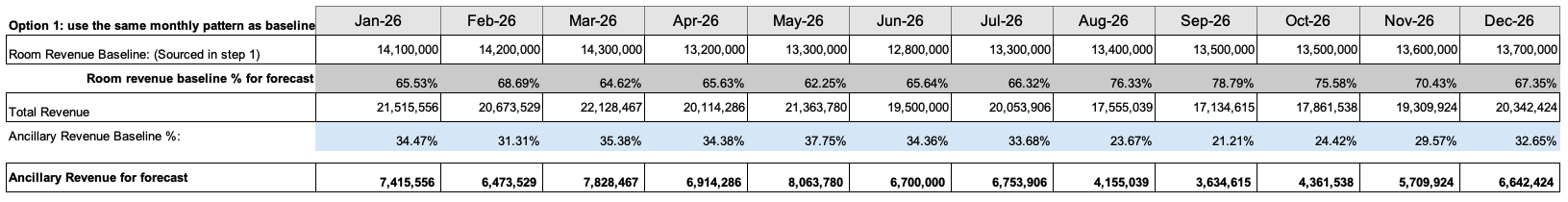
Formula: Ancillary revenue for forecast equals Room revenue for forecast divided by Room revenue baseline % multiplied by Ancillary revenue baseline %.
If EP is set-up to distribute the total ancillary revenue evenly across months (using annual average from baseline) then the calculation is performed as shown below:
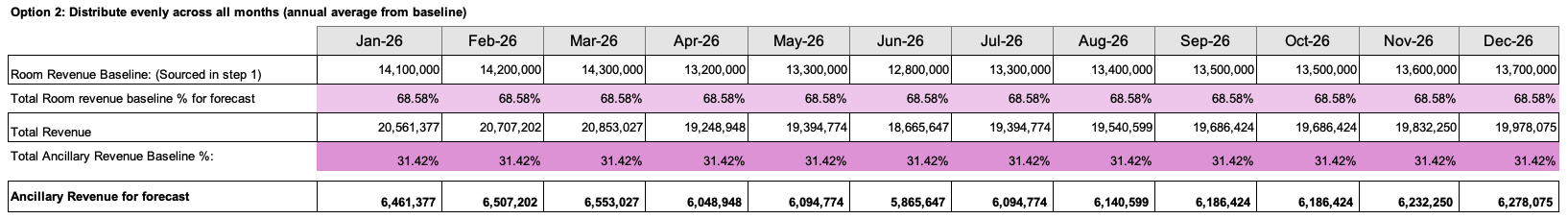
Formula: Ancillary revenue for forecast (annual average baseline) equals Room revenue for forecast divided by Room revenue annual baseline % multiplied by Ancillary revenue annual baseline %.
Step 3: Apply growth adjustment to ancillary revenue
It is customary that non-room revenue will grow in the same proportion as room revenue. If this is not the case and you expect that there will be additional growth in the non-room departments, you can set the additional growth percentage that you expect in rule 2 under ancillary revenue settings.
The percentage you’ve selected here will then be used to increase the non-room revenue as calculated below.

Formula: Ancillary Revenue for forecast with growth expectation equals Ancillary revenue for forecast (no growth expectation) multiplied by (one plus the growth expectation). (this then becomes ancillary revenue for forecast in subsequent calculations)

Step 4: Split Ancillary revenue into divisions
The divisions visible here are the divisions set up in PMI.
Before the forecasted ancillary revenue can be separated into divisions, the split ratio that was used in the historical year that was selected in rule 1 needs to be determined.
These proportions will then be applied to the forecasted total revenue (calculated in step 3) to calculate the forecasted divisional revenue.
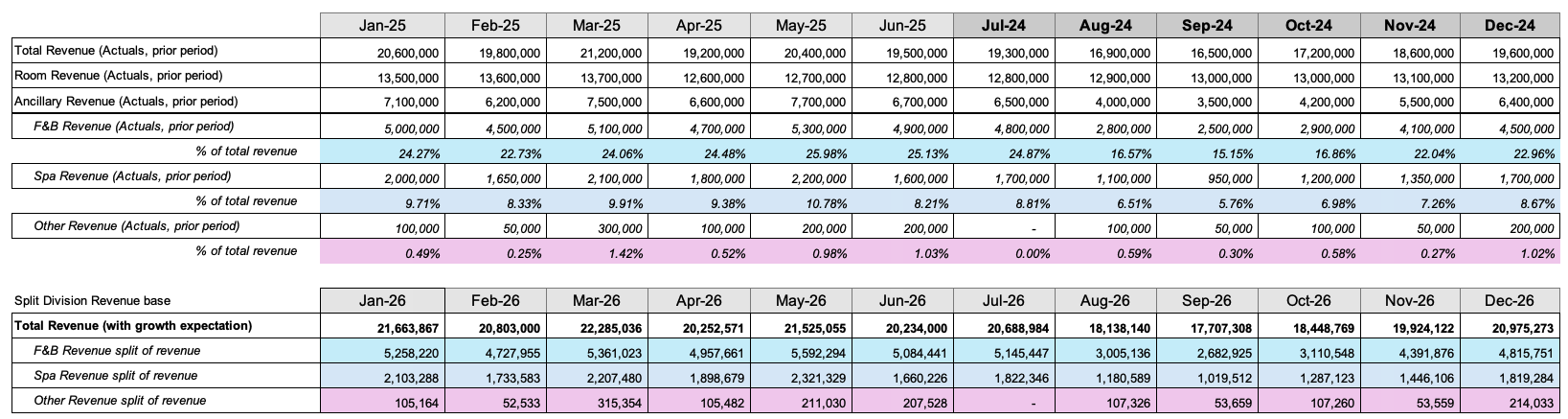
Users can specify the minimum percentage of total revenue per division, to avoid situations where an abnormally low month is present in the historical year (eg: Spa was closed for renovations in May). This setting can be found on the “Rules for general settings” page. For any month where the divisional percentage is less than the specified percentage, a yearly average will be used instead of the specific monthly percentage.
Step 5: Split divisional revenue into departments
EP calculates historical department revenue ratio against the total divisional revenue less departments with specified exceptions.
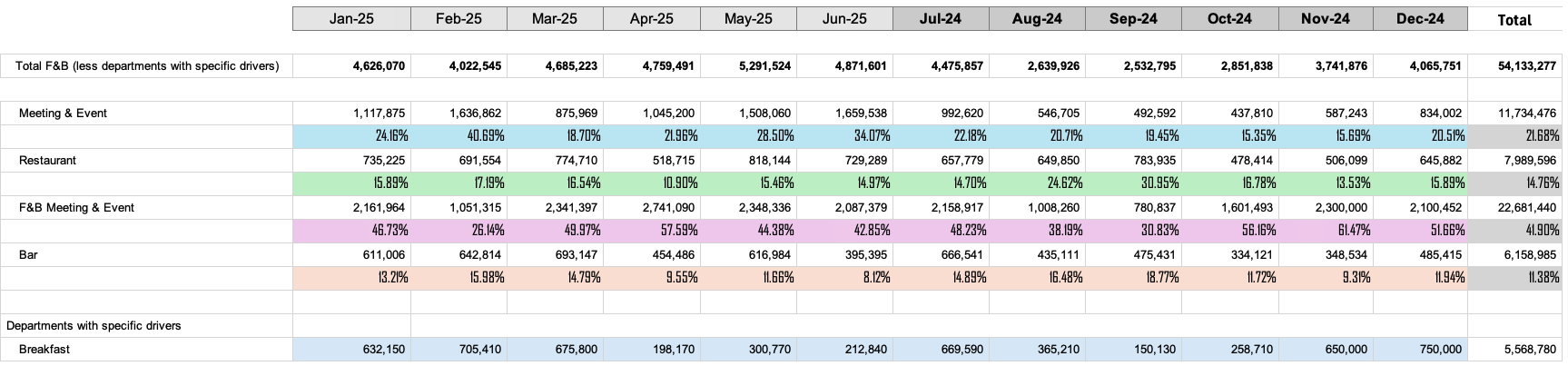
Departments with specified exceptions in rule 5 of ancillary revenue set-up are calculated first.
This revenue is then removed from total divisional revenue and the remainder is divided to the remaining departments based on the ratios calculated.
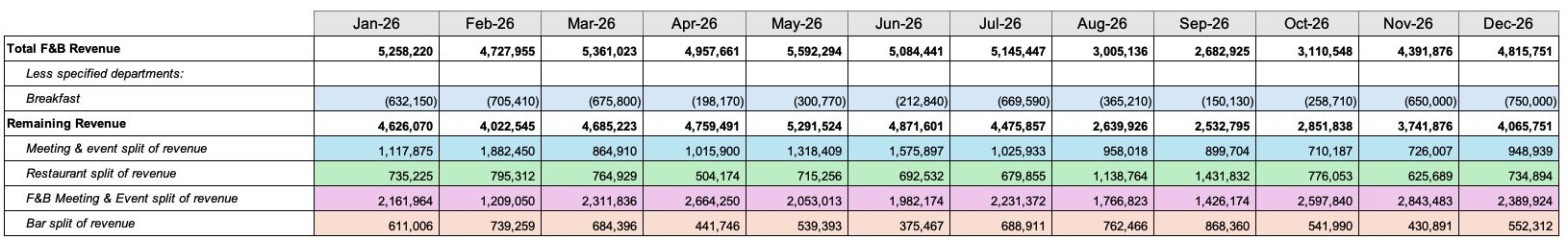
Step 6: Segment departmental revenue (if applicable)
For departments where the “Segments” option under Settings in the Budget & forecast page has been selected, the departmental revenue calculated in rule 4 will be split into these segments.
Calculation method will be the same method visualized in Step 5, but without exceptions. (It is not possible to set exceptions for segments)
Step 7: Calculate productivity
Example below shows 2 departments calculating productivity based on their cost driver using last available actual period.
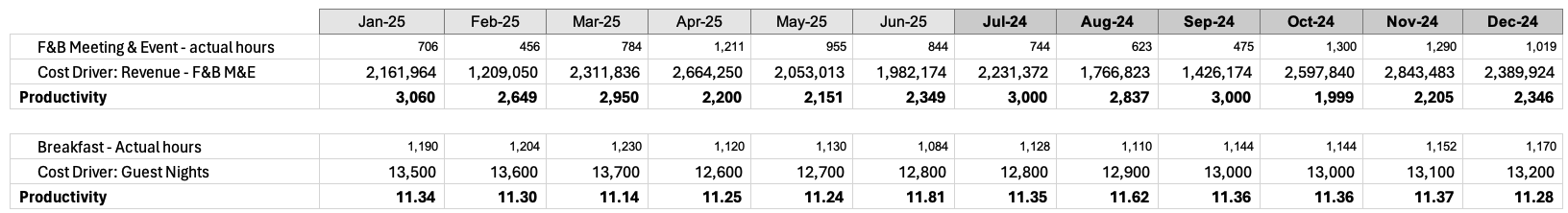
Under Labor hours set-up it is also possible to add a productivity adjustment %. This will be applied to the productivity for all historically calculated departments.
Step 8: Calculate forecasted labor hours
The calculated historical productivity rates are then applied to the forecasted cost drivers for each department to determine the forecasted hours for each department. If a department has an exception to calculate based on a fixed number of hours per day, then this amount will be multiplied by the days in the month to determine the monthly amount.
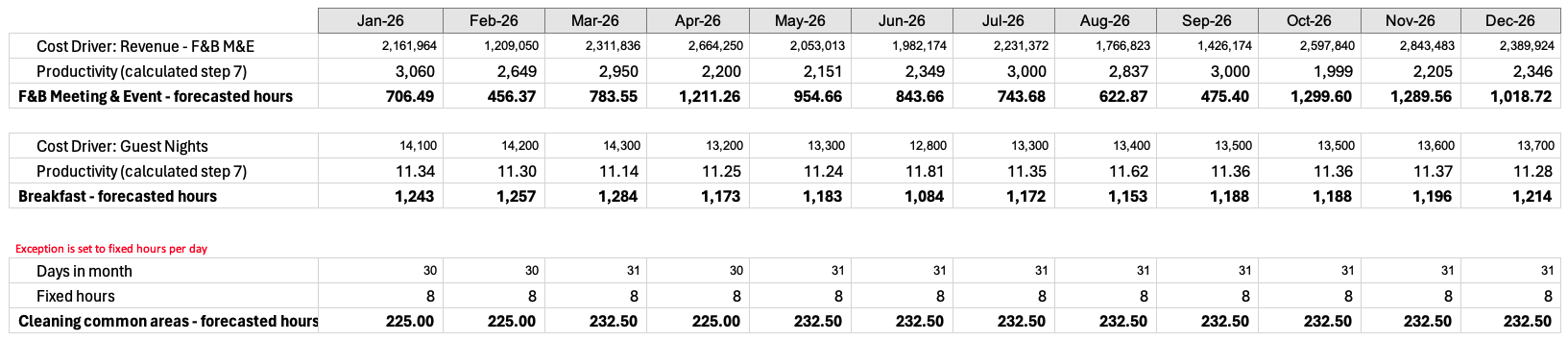
Note: If schedule horizon for a labor department overlaps with a month in the forecast then EP will not overwrite the forecast for this month.
Step 9: Allocate outsourced labor hours
For departments which have outsourced hours, EP will check the historical ratio between outsourced and non-outsourced hours.
It will allocate the forecasted hours between outsourced and non-outsourced hours in the forecast based on the historical percentage.
Interpretation
When EP has been run and completed its forecast, the forecasted revenue figures will be available for review in modules which populate forecast figures. (Management perspective, Flash report, Live forecast, etc)
Forecasted hours will be available for review in modules where forecasted hours can be viewed. (Labor cockpits, Management perspective, Staffing, etc)
Common mistakes
– Not verifying the source of room revenue baseline (e.g., using outdated actuals).
– Misapplying growth percentages or productivity ratios.
– Overlooking fixed hour overrides in labor forecasting.
– Overlooking schedule horizons in labor cockpits
Use cases
EP is used by finance and operations teams to forecast:
– Ancillary revenue based on room revenue.
– Labor hours by department and division.
– Outsourced vs. in-house labor allocation.
Useful for extending forecasting period for hotel without requiring extensive operational administration for periods with limited visibility. (eg: periods beyond the next 3 months)
Eg: Hotel GM, controller, or HQ can run forecasts for Hotel for periods further away from current date (where there is less current operational information available) without requiring the full operational team to update their forecasts.
Cross-references
See also:
– Express planner overview
– How to configure express planner settings
– How to run express planner
Related features and modules
Modules:
– Budget and Forecast
– Schedule